A charge controller, charge regulator or battery regulator limits the rate at which electric current is added to or drawn from electric batteries. It prevents overcharging and may prevent against over-voltage, which can reduce battery performance or lifespan, and may pose a safety risk. It may also prevent completely draining ("deep discharging") a battery, or perform controlled discharges, depending on the battery technology, to protect battery life. The terms "charge controller" or "charge regulator" may refer to either a stand-alone device, or to control circuitry integrated within a battery pack, battery-powered device, or battery re-charger.
2 TYPES OF CHARGE CONTROLLER:
MPPT
This section covers the theory and operation of "Maximum Power Point Tracking" as used in solar electric charge controllers.
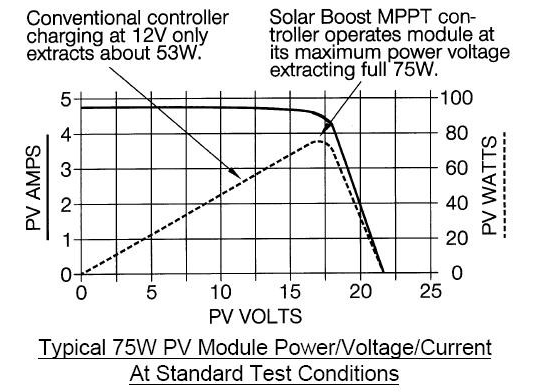
A MPPT, or maximum power point tracker is an electronic DC to DC converter that optimizes the match between the solar array (PV panels), and the battery bank or utility grid. To put it simply, they convert a higher voltage DC output from solar panels (and a few wind generators) down to the lower voltage needed to charge batteries.
(These are sometimes called "power point trackers" for short - not to be confused with PANEL trackers, which are a solar panel mount that follows, or tracks, the sun).
PWM
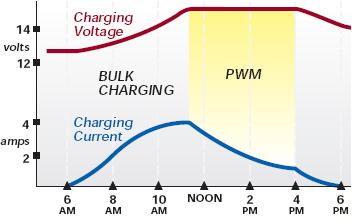
Quite a few charge controls have a "PWM" mode. PWM stands for Pulse Width Modulation. PWM is often used as one method of float charging. Instead of a steady output from the controller, it sends out a series of short charging pulses to the battery - a very rapid "on-off" switch. The controller constantly checks the state of the battery to determine how fast to send pulses, and how long (wide) the pulses will be. In a fully charged battery with no load, it may just "tick" every few seconds and send a short pulse to the battery. In a discharged battery, the pulses would be very long and almost continuous, or the controller may go into "full on" mode. The controller checks the state of charge on the battery between pulses and adjusts itself each time.
PWM charging helps the battery to reach full charge by pulse charging, The PWM pulses slower, gradually tapering off the charge as the battery fills with amps. Pulsing is good for the batteries because it mixes the electrolyte cleaning the lead plates and preventing sulphation. This technology is used in most all charge controllers.

No comments:
Post a Comment